ML in the Browser
with Tensorflow.js
Ed Atrero
Weedmaps Tech Meetup
Machine Learning
Computer Vision
Image Classification
Demo
Machine Learning
Computer Vision
Image Classification
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Convolutional Neural Networks
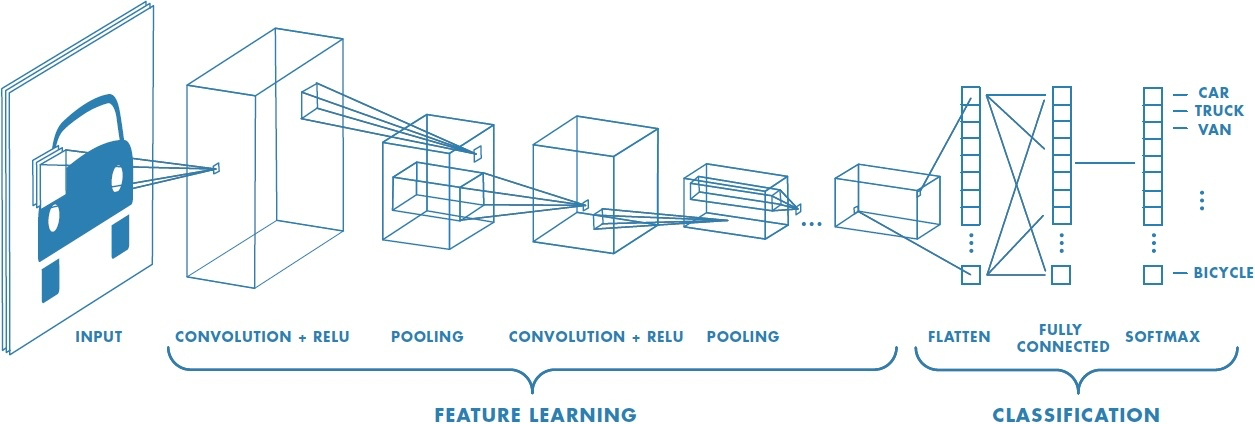
What is a Convolution?
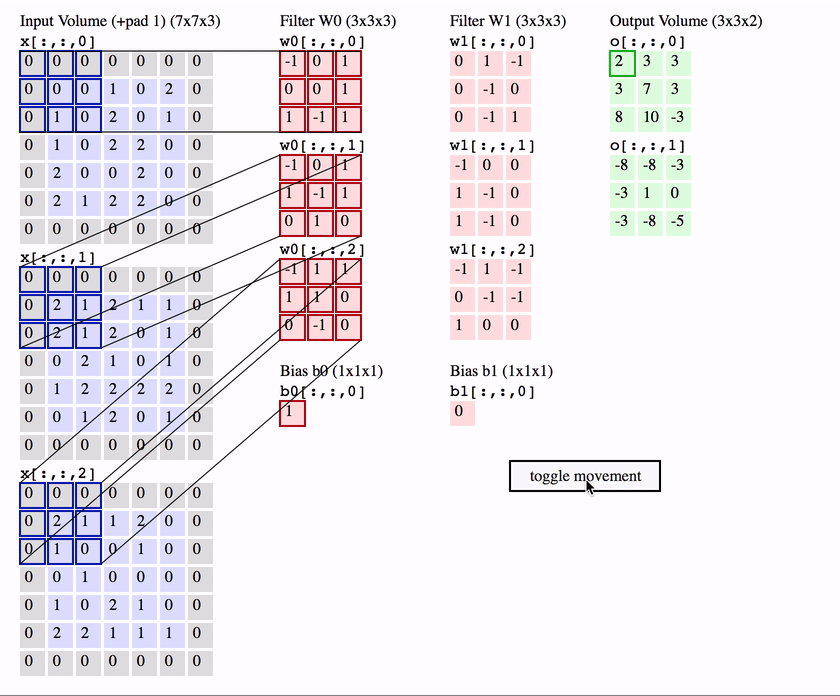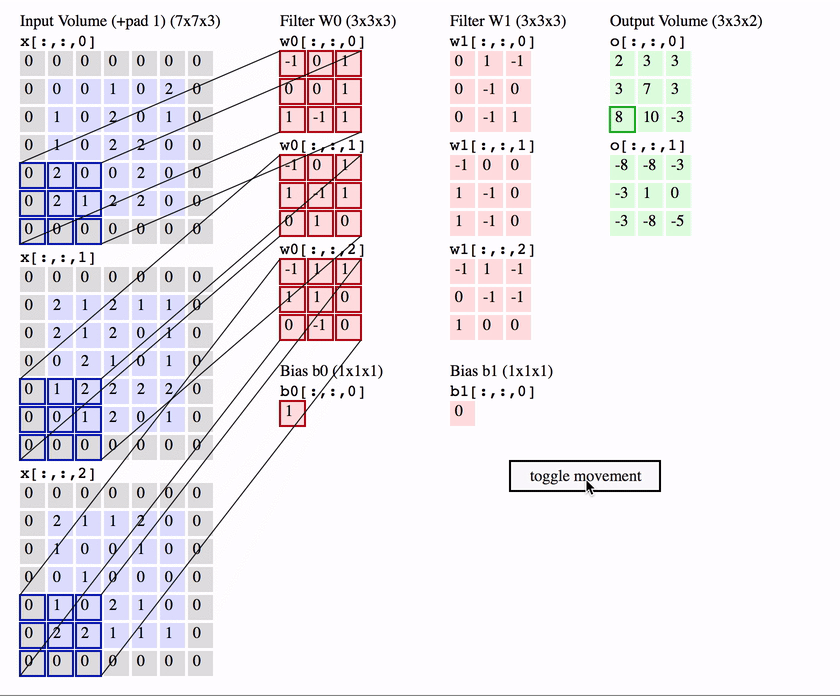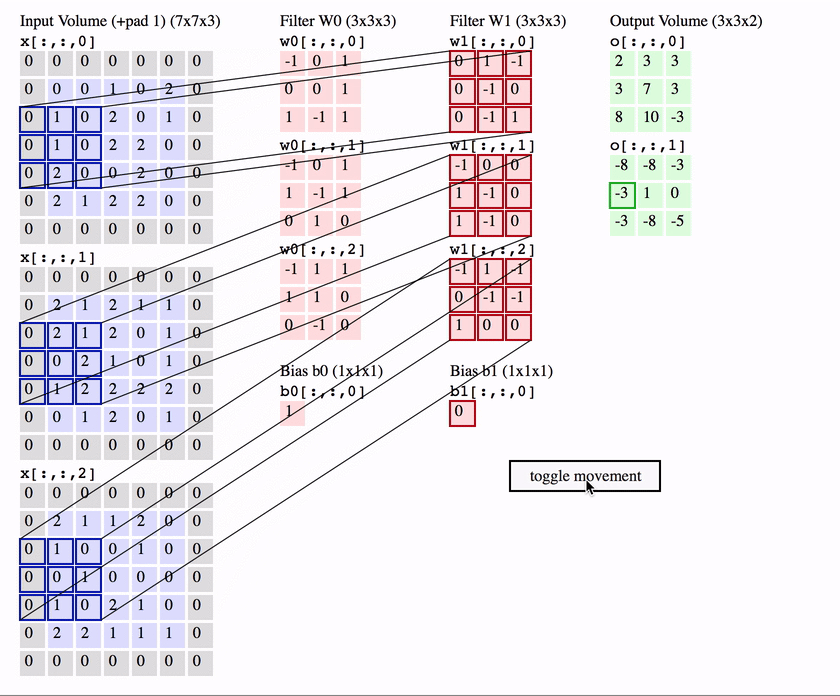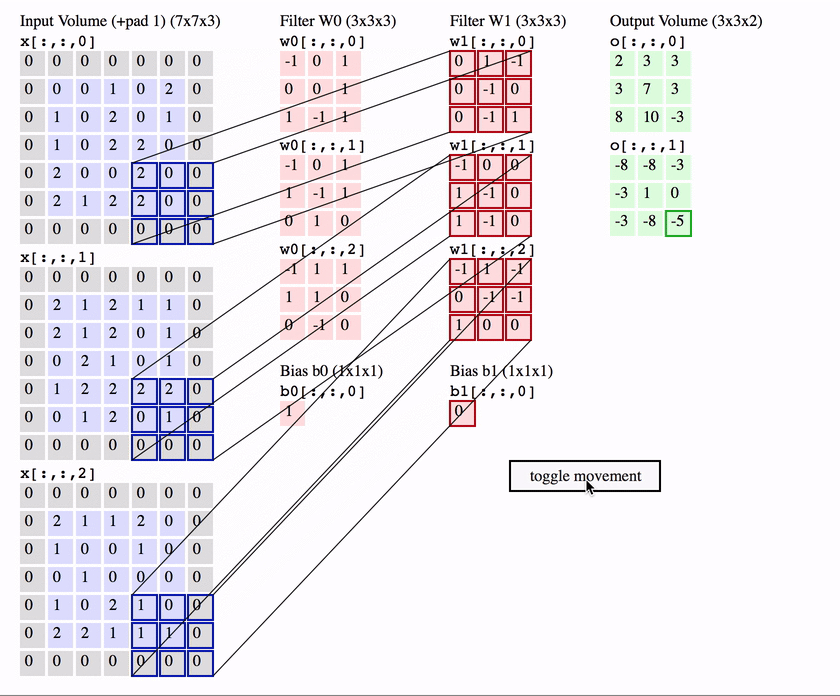
weights

Machine Learning Steps:
1. Model
2. Train
3. Predict
Transfer Learning

Tensorflow
Library released by Google Brain team in 2015.
Processing multidimensional arrays (tensors)
CPUs, GPUs, TPUs
Tensorflow.js
The JS version of tensorflow
Uses GPU via WebGL shaders
ML portion of the demo in less than 100 lines
Model
Training
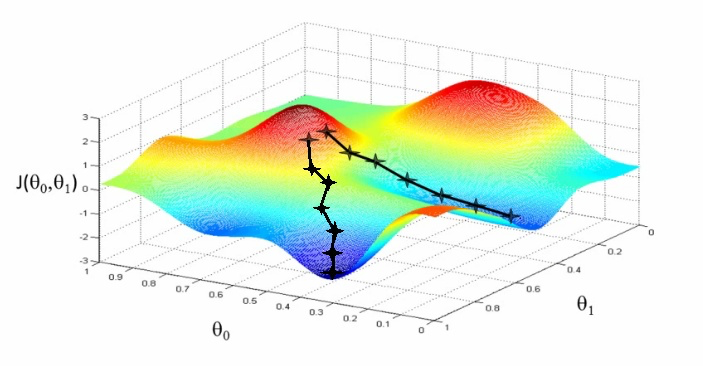
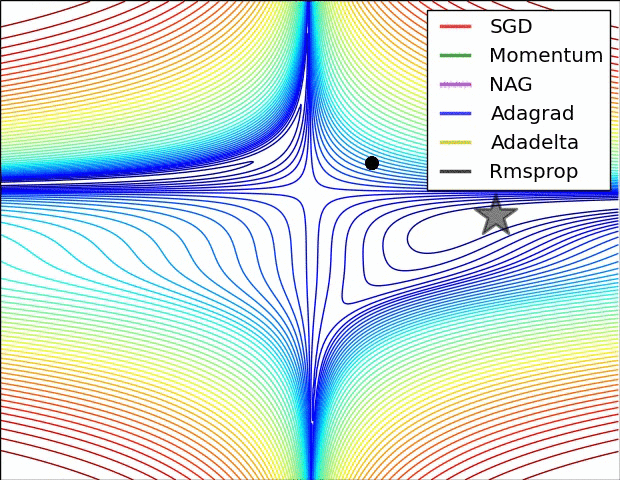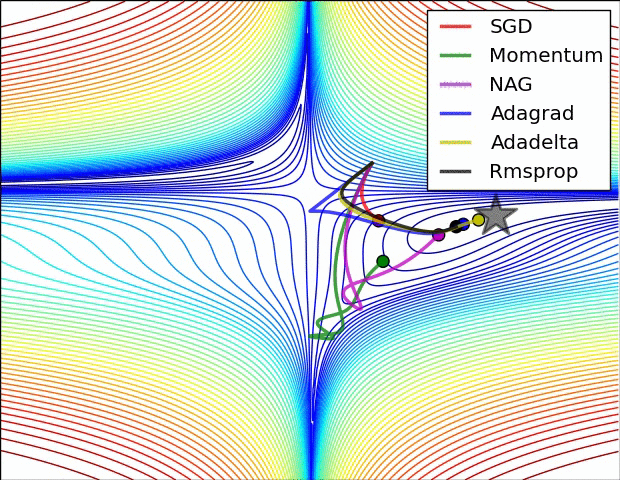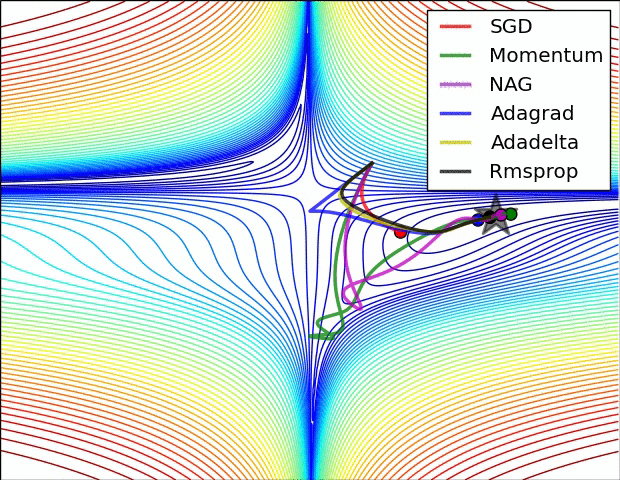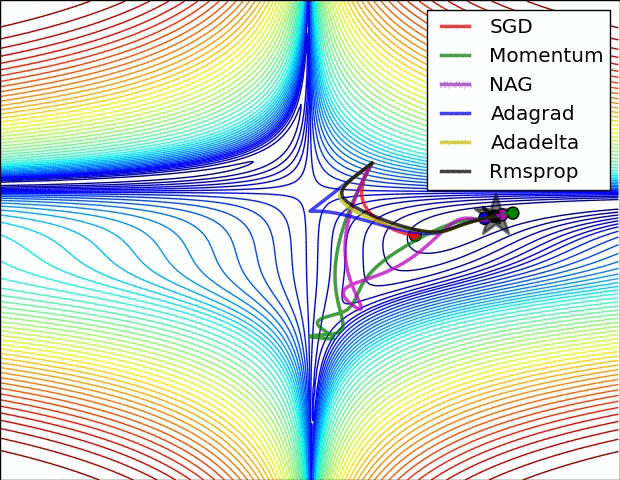
Stochastic Gradient Descent
Predict
